Read and report vaccine reactions, harassment and failures.
Smallpox & Monkeypox (Mpox) Disease & Vaccine Information
Smallpox/Monkeypox (Mpox): The Disease
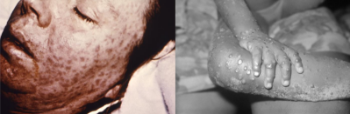
Smallpox is an illness caused by the variola virus, a virus belonging to the orthopoxvirus family of viruses. Symptoms of the disease include head and backache, anorexia, severe abdominal pain, vomiting, extreme exhaustion, malaise, chills, rash, and high fever. When the fever resolved, rash lesions would begin to develop and appear in the back of the mouth, behind the oral cavity (oropharynx), followed by the face, arms, legs, and then would have spread to the torso, palms and soles. When smallpox was circulating in the environment, there were several forms of the disease, with some more severe and life-threatening than others.
Monkeypox (Mpox) is an infection caused by the mpox virus and like smallpox is also a member of the Orthopoxvirus family. Symptoms of mpox are similar to smallpox but are generally milder. Individuals infected with mpox usually present with headache, backache, fever, chills, muscle aches, extreme fatigue and exhaustion. Swelling of the lymph nodes also occurs, which is a symptom not present with smallpox infection. A rash, which usually appears on the face, begins within one to three days of fever, and spreads throughout the body. Mpox is rare and is generally found in Africa, although cases and outbreaks have occurred globally. Learn more about smallpox/monkeypox…
Smallpox/Monkeypox (Mpox): The Vaccine
There are two smallpox vaccines approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA): ACAM 2000, a live smallpox (vaccinia) vaccine, and JYNNEOS, a live, non-replicating, smallpox and monkeypox (mpox) vaccine. A third vaccine, Aventis Pasteur Smallpox Vaccine (APSV), is an unapproved vaccine that has been added to the Strategic National Stockpile (SNS). Learn more about smallpox/monkeypox vaccine…
Smallpox/Monkeypox(Mpox) Quick FactsSmallpox/Mpox Disease
- Smallpox is an illness caused by the variola virus, belonging to the orthopoxvirus family. There are several forms of smallpox illness, including Variola Major, modified-type smallpox, hemorrhagic smallpox, malignant (flat-type) smallpox, and Variola Minor. Variola Major was the most common form of the illness when smallpox was circulating in the environment. Initial symptoms of smallpox illness included anorexia, vomiting, malaise, high fever, chills, headache, backache, severe abdominal pain, pharyngitis, and extreme exhaustion. A rash might have also been visible in light-skinned individuals. Rash lesions would begin after the fever resolved and appear in the back of the mouth, behind the oral cavity (oropharynx), followed by the face, arms, and legs, and would eventually spread to the torso, palms, and soles.
- Monkeypox (Mpox), another orthopoxvirus, is similar in symptoms to smallpox but generally milder. With mpox, infected individuals develop swelling of the lymph nodes. Continue reading quick facts…
Smallpox/Monkeypox Vaccine
- There are two smallpox vaccines approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The ACAM 2000 vaccine is a live smallpox (vaccinia) vaccine approved for use in persons considered at high risk for smallpox infection. The JYNNEOS vaccine is a live, non-replicating, smallpox and monkeypox (mpox) vaccine and approved for use in adults 18 years of age and older who are considered to be at high-risk of smallpox or mpox. The FDA has also issued an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for the use of the JYNNEOS vaccine to be given subcutaneously to high-risk persons under the age of 18, and intradermally (between the skin layers) to high-risk persons aged 18 and older.
- Serious adverse events reported following ACAM 2000 vaccination include encephalitis (brain inflammation), encephalomyelitis (inflammation of brain and spinal cord), encephalopathy (disease of brain causing alteration of brain function or structure), generalized vaccinia (systemic spread of the virus from the inoculation site), progressive vaccinia (vaccinia necrosum – death of bodily tissues), severe vaccinial skin infections, eczema vaccinatum, erythema multiforme major including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (severe and potentially life threatening skin and/or mucus membrane lesions), blindness, and fetal death in pregnant women. These complications have the potential to cause severe disability, permanent neurological deficits, and death. Serious adverse events reported during clinical trials for the JYNNEOS vaccine noted in the product insert include Crohn’s disease, sarcoidosis (inflammatory disease affecting organs), extraocular muscle paresis (weakening of eye muscles) and throat tightness. Continue reading quick facts…
NVIC encourages you to become fully informed about Smallpox/Monkeypox (Mpox) and the Smallpox/Monkeypox(Mpox) vaccine by reading all sections in the table of contents provided on this webpage. NVIC provides highly referenced information that allow the public to click through to the reference material used to compile this information, such as the manufacturer product information inserts maintained on the U.S. Food & Drug Administration's website and vaccine information statements issued by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. As you consider vaccination, we encourage the public to educate themselves on the disease and vaccine and to speak with one or more trusted health care professionals before making a vaccination decision for yourself or your child. This information is for educational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice.



