To activate and view hyperlinked references, please click once and then click any superscripted number below to access a hyperlinked reference, or scroll down to the bottom of the article to view all hyperlinked references.

Since I was asked to make a presentation about vaccine exemptions in 1997 at the Department of Health and Human Services in Washington, D.C., I have publicly defended the informed consent principle, which was defined as a human right at the Doctors Trial at Nuremberg in 1947. 1 Informed consent means you have the right to be fully informed about the benefits and risks of a medical intervention and the freedom to make a voluntary decision about whether or not to accept those risks without being coerced or punished for the decision you make. Informed consent applies not just to risks taken by participants in scientific experiments, but also to risks taken by patients under the care of physicians. 2 3 4 5
Informed Consent Principle Applies to All Medical Risk-Taking
Today, when a person publicly advocates for informed consent protections in vaccine laws, an “anti-vaccine” label is usually immediately applied to shut down any further conversation. 6 7 Perhaps because a conversation about ethics opens up a wider conversation about freedom.

The right and responsibility for making a decision about risk taking rightly belongs to the person taking the risk. When you become informed and think rationally about a risk that you or your minor child may take - and then follow your conscience - you own that decision. And when you own it, you can defend it. And once you can defend it, you will be ready to do whatever it takes to fight for your freedom to make it, no matter who tries to prevent you from doing that.
Never Do Anything Against Conscience
Albert Einstein, who risked arrest in Germany in the 1930’s when he spoke out against censorship and persecution of minorities, said, “Never do anything against conscience even if the State demands it.” 8
There is no liberty more fundamentally a natural, inalienable right than the freedom to think independently and follow our conscience when choosing what we are willing to risk our life or our child’s life for.
Because the journey we take on this earth is defined by the choices we make. If we are not free to make choices, the journey is not our own. The choices we make that involve risk of harm to our physical body, which houses our mind and spirit, those are among the most profound choices we make in this life.
Vaccine Risks Not Being Borne Equally By Everyone in Society

So, vaccination must remain a choice because it is a medical intervention performed on the body of a healthy person that carries a risk of injury or death. 9 10 And while we are all born equal, with equal rights under the law, we are not born all the same. Each one of us is born with different genes and a unique microbiome influenced by epigenetics that affects how we respond to the environments we live in. 11 12
We do not all respond the same way to pharmaceutical products like vaccines, so vaccine risks are not being borne equally by everyone in society.
Why should the lives of those vulnerable to vaccine complications be valued any less than those vulnerable to complications of infections? And why should people not be free to choose to stay healthy in ways that pose far fewer risks?
Vaccines Carry Risks and Do Not Guarantee Protection
The act of vaccination involves the deliberate introduction of killed live attenuated or genetically engineered microbes into the body of a healthy person, along with varying amounts of chemicals, metals, human and animal RNA and DNA and other ingredients 13 that atypically manipulate the immune system to mount an inflammatory response that stimulates artificial immunity. 14

But there is no guarantee that vaccination will not compromise biological integrity or cause the death of a healthy or vaccine vulnerable person either immediately or in the future. There is also no guarantee that vaccination will protect a person from getting an infection with or without symptoms and transmitting it to others. 15
Vaccine Science Gaps, Doctors Cannot Predict Who Will React
Reports published by physician committees at the Institute of Medicine confirm that vaccines, like infections, can injure and kill people but that:
- very little is known about how vaccines or microbes act at the cellular and molecular level in the human body; 16 17 18 and
- the Institute of Medicine confirms that an unknown number of us have certain genetic, biological and environmental susceptibilities that make us more vulnerable to being harmed by vaccines, but doctors cannot accurately predict who we are; 19 20 and
- that clinical trials of experimental vaccines are too small to detect serious reactions before they are licensed; 21 22 and
- that the U.S. recommended child vaccine schedule through age six has not been adequately studied to rule out an association with allergies, autoimmunity, learning and behavior disorders, seizures, autism and other brain and immune dysfunction. 23
Yet, with these large gaps in scientific knowledge, government health officials direct physicians to vaccinate 99.99 percent of children regardless of known or unknown risks. 2425
Government Licensed Vaccines “Unavoidably Unsafe”
Therefore, vaccination is a medical procedure that can be termed experimental each time it is performed on a person. By extension, “no exceptions” mandatory vaccination laws create a de facto uncontrolled, population based scientific experiment that enrolls every child at birth and never ends, sacrificing an unknown number of vaccine vulnerable children.

Further, the US Congress and Supreme Court have declared federally licensed vaccines to be “unavoidably unsafe,” removing civil liability from doctors who give vaccines and drug companies that sell vaccines in what has become a very lucrative multi-billion dollar business in the U.S. 26 27 At the same time, the federal vaccine injury compensation program created by Congress in 1986 that was supposed to be a no-fault alternative to a lawsuit – not instead of a lawsuit – has been gutted by federal agencies so that, today, almost no child receives compensation when they are hurt by vaccines. 28
Now, a global vaccine injury compensation program is being created to shield multinational corporations from liability for injuries caused by the hundreds of new genetically engineered vaccines governments will mandate in the future. 29 30 31 32 33 34
All this, while medical trade groups affiliated with industry and government join forces to lobby for removal of flexible medical, conscientious and religious belief exemptions from state health laws, 35 as was done in California in 2015, 36 so that those who refuse government endorsed vaccines for themselves or their minor children can be denied an education, employment, health care and other civil rights.
Utilitarianism Should Not Be Foundation of Public Health Law
In 1996, when I was in the Holocaust Museum in Washington, D.C. attending a conference on the role of physicians and scientists implementing public health policy during the Third Reich, I looked up and saw an inscription that took my breath away. It said, “the first to perish were the children…from these a new dawn might have risen.”

This commentary, which I originally presented in March 2017 at the inaugural meeting of Physicians for Informed Consent in California, 37 is dedicated to mothers and fathers, whose children died or became brain injured when the risks of vaccination turned out to be 100 percent.
I am arguing that the consequentialist theory of utilitarianism 38 39 40 is a pseudo-ethic that must be rejected as the moral foundation of public health policy and law so it can be replaced with a compassionate ethic grounded in respect for the human right to autonomy and informed consent to medical risk taking, including vaccine risk taking.
Pediatrician Censored for Reporting Infant Deaths After DPT Shots
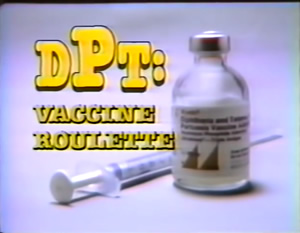
I remember the day in the spring of 1982, when I was a young mother with a four year-old son struggling with the effects of a serious DPT vaccine reaction. I had just seen the NBC television documentary DPT: Vaccine Roulette 41 and was networking with parents of DPT vaccine injured children in the Washington, D.C. area when I decided to attend a press conference at the American Academy of Neurology to hear a young pediatric neurologist talk about his study in which two thirds of the babies, whose deaths were classified sudden infant death syndrome, had died within three weeks of a DPT shot.
This pediatrician was concerned that DPT vaccine may be a major unrecognized cause of early childhood death, including SIDS, and he suggested that more research be done. As soon as he finished, his physician colleagues launched a vicious attack on his professional expertise and personal integrity that left him physically trembling in a cold sweat. I had never seen anything like it.
During the break, I was approached by a PhD scientist who, at the time, worked for the National Academy of Sciences. This scientist asked me why I was there and I told him I wanted to know more about DPT vaccine because, when I was taking my baby to be vaccinated, I had no idea that vaccines – which were supposed to keep children healthy - could actually kill them.
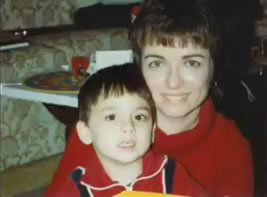
He got this quizzical look on his face and said something to the effect that it only happens once in a million kids. And instinctively I said, but if a vaccine kills even one, how can all children be legally required to get it? He looked surprised, uncomfortable, and walked away mumbling something about vaccine benefits far outweigh the risks, and sometimes we have to make sacrifices for the greater good.
And I thought to myself, but the benefits didn’t outweigh the risks for my child or for the babies who died after DPT shots in the study that young doctor tried to talk about before he was figuratively lynched for suggesting that DPT vaccine benefits might not outweigh the risks.
And why was my child’s health sacrificed without my knowledge or permission, and what is “the good” that is made greater by child sacrifice, and who defines it as “good”?
Playing DPT Vaccine Roulette with My Son’s Life
When I became a Mom in 1978, my son, Chris, was the light of my life. Happy, healthy and precocious, he was saying words at seven months,
speaking in full sentences by age two and identifying words in the books we read together every day. One doctor told me he was cognitively gifted.
But everything changed in 1980 when, within hours of his fourth DTP shot, I witnessed the eyes of my two and a half year old son roll back in his head and his head fall to his shoulder as if he had fallen asleep sitting up. I carried him, pale and limp, to his bed, where he did not move for hours. I thought to myself, oh, he is tired and just taking a really long nap, or maybe he is coming down with a cold.
And when I finally was able to wake him but he couldn’t sit up or walk or speak coherently, when he had terrible diarrhea and only stayed conscious for a few minutes before falling into 12 more hours of deep sleep, I did not understand that I had witnessed a classic post-DPT vaccine convulsion and “hypotonic/hyporesponsive reaction and brain inflammation. 42 43 44 45 Chris was not just taking a really long nap, he was unconscious in his bed and could have died that day.
I did not know because my pediatrician had told me nothing about how to recognize a vaccine reaction, including symptoms of encephalitis - brain inflammation that has been a well-documented complication of vaccination for two centuries. 46 47 48 49 I did not know that the unusual local reaction after his third DPT shot was a warning sign or that our family history of severe allergies and autoimmune disorders could increase vaccine risks. 50 51 52 53 54 55 56
Even though I came from a family of doctors and nurses, had a college degree and had worked at a teaching hospital – like most parents back then I believed that vaccines were 100 percent safe and effective.
And in the following days and weeks, when Chris could no longer concentrate or do what we could do before, when his personality changed and he was constantly sick with ear and respiratory infections, diarrhea, new food allergies and severe weight loss, my family and I could not understand why Chris had regressed physically, mentally and emotionally and become a totally different child. His doctors told us there was no explanation and said I should take him home and love him.
Eighteen months later, when I, and millions of other parents in America, watched the Emmy award winning “DPT Vaccine Roulette,” 57 I called the TV station and asked if I could have copies of the medical literature used to anchor the documentary.
And it was in my living room as I read case history descriptions of DPT vaccine injury and death in the pages of Pediatrics 58 59 60 and the British Medical Journal 61 62 63 and New England Journal of Medicine 64 that exactly matched the symptoms of brain inflammation I witnessed my son suffer that day, it was then I knew that physicians had been talking in medical journals for more than 50 years about the fact that pertussis vaccine could brain damage children, but no one had informed the mothers dutifully bringing their children for DPT shots legally required to go to school.

As I tried to help my son cope with multiple learning disabilities that included dyslexia, fine and gross motor skill delay, auditory processing and attention deficit, and short term memory delays so severe they confined him to a special ed classroom throughout his public school education, and as I interviewed hundreds of mothers for the book DPT: A Shot in the Dark, I came to know many families whose children had died or were much more severely vaccine injured than my child. 65 66
Chris has worked hard to compensate for his learning disabilities and he is a productive member of society today; but many vaccine injured children, tragically, are not. 67
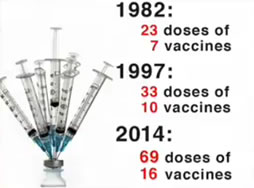
My son is among the walked wounded in what has become an unprecedented and still unexplained chronic disease and disability epidemic now plaguing millions of children and young adults in America. 68 It is an epidemic of learning disabilities, ADHD, asthma, seizures, autism, diabetes, depression, and other types of brain and immune dysfunction marked by chronic inflammation in the body that has perfectly coincided with the tripling of the numbers of vaccines given to children – from 23 doses of seven vaccines starting at two months through age six in the early 1980s - to the current 69 doses of 16 vaccines starting on the day of birth with 50 doses given before age six. 69 70
In 1982, it was my curiosity about the truth of the matter that pushed me to research the science, policy, law, ethics, history and politics of vaccination and spend two decades participating in public engagement projects at the Institute of Medicine and Department of Health and Human Services, where I served as a consumer member on vaccine advisory committees at the FDA and CDC, 71 a journey that has now spanned half my life.
So, I offer you my perspective from that vantage point.
Philosophy: Love of Wisdom
Here we are in the 21st century, where the electronic communications revolution has created a virtual global public square on the World Wide Web,
where more than three billion people are talking to - and sometimes yelling at - each other about ideas, values and beliefs, just like they did in the public squares of ancient Athens and Rome, and in universities, newspapers, and on radio and television since then.
Throughout recorded history, people have disagreed with each other about how to answer big questions, like:

- Where do we come from?
- Are we only physical matter or do we have an immortal soul, a consciousness that survives physical death?
- What is truth and how can we know it?
- What is ethical behavior and how can we define it?
Most of the formal debates about these questions have been described in the history of philosophy, 72 which the ancient Greeks defined as “love of wisdom,” that included study of knowledge; reasoning; nature of being or metaphysics; aesthetics; and ethics.
The philosophy of science emerged as a separate discipline in the 18th and 19h centuries after mathematicians and astronomers mounted a successful challenge to the authority of organized religion.
Science Now Dominates, Affect Cultural Values & Laws
Since then, science has invaded and dominated every other branch of philosophy. As we are reminded every day in so many ways, science and math rule, and scientific evidence determines what is true and what is not. In fact, those who practice and submit to the authority of science insist that not only must science be used to define all truth, but leaders in science and medicine are authorities who should define “the good,” that is, define moral behavior and what kind of cultural values we should have, and what kind of beliefs we should be allowed to hold and teach our children, and what kind of laws should be passed in order to limit the ability of individuals to make “unscientific” choices that presumably endanger the public health and welfare. 73

That’s a whole lot of pressure for many physicians, who do not want to be put on a pedestal and required to exercise that kind of authority over the lives of fellow human beings because - first and foremost - it interferes with developing a relationship with patients based on mutual respect, trust and shared decision making.
But, the stark reality is that the scientification of every branch of philosophy has elevated prominent scientists and physicians promoting “consensus science” into positions of authority, whose judgment should never be questioned. Long held cultural values, such as respect for freedom of thought, speech, conscience and religious belief are being called into question, which, in turn, affects court decisions and the making of laws.
No where is this more visible than in public health law using the materialist philosophy of utilitarianism to legally require all Americans to use an increasing number of vaccines without their voluntary informed consent.
So how did we get here? How did science come to dominate how we define what is true and good for the individual and society in the 21st century?
Old Arguments About What Is True and Good
Although conversations about the meaning of life and what is good started before written history and is embedded in tenets of five surviving major religions - Hinduism, Buddhism, Islam, Judaism, and Christianity - it was the classical Greek philosophers who began recording the debate.
Socrates, Plato and Aristotle believed that we are physical matter animated by a vital spirit, and we can use innate knowledge and reason to perceive what is good.
Epicurus disagreed and said humans are only physical matter and have no spirit or innate knowledge and that seeking pleasure and avoiding pain is the highest good and guide to moral behavior.
For 1500 years following the birth of Christ, the highest good was defined as knowing and loving God in western cultures adopting Judeo-Christian moral values - until the Scientific Revolution when 15th and 16th century scientists Copernicus, Galileo, Newton and Francis Bacon developed methods for determining what is true that put the existence of God on trial, along with the definition of what is good.

Although between the 16th and 19th centuries, Descartes, Locke, Kant, Hegel and other philosophers argued that humans are both physical matter and spirit and can use reason to understand scientific truth, as well as to perceive the natural law that serves as a guide to what is good, the materialist philosophers Hobbes, Hume, Bentham, Comte, Marx and Nietzsche argued that science proves there is no God or human spirit because we are only physical matter, and there are no absolute moral values but, rather, science can be used to define what is true and good.
This included the idea that a mathematical equation can be used to judge whether or not an individual action, government policy or law is moral.
The authors of the U.S. Declaration of Independence agreed with the philosophers who argued that humans have a physical body animated by a soul or spirit, and that we can use reason given to us by God to perceive the natural law, which includes natural rights, that belong to all individuals and limit the authority of government.
The Bill of Rights in the US Constitution contains strong language protecting exercise of natural rights. 74 These have been defined internationally as human rights, including freedom of thought, speech, conscience and religious belief. 75 76
Utilitarianism: Mathematics, Vaccination & Public Health Rising
But today, it is not respect for natural rights that guides public health policy in the U.S., it is the philosophy of utilitarianism, created by Jeremy Bentham, a 19th century British attorney and social reformer. 77 78 Bentham mocked the U.S. Constitution for mentioning God and affirming natural rights protected in the First Amendment.
Like Comte, Marx and Nietzsche who followed him, Bentham did not believe that man has a soul or innate intelligence, so he returned to the hedonistic Epicurean philosophy of maximizing pleasure and minimizing pain to define what is good.
Bentham’s utilitarianism uses a mathematical equation that judges the rightness or wrongness of an action by its consequences. Bentham said that an action is only moral or ethical if it results in the greatest happiness for the greatest number of people. With its emphasis on numbers of people, Bentham created utilitarianism primarily as a guide to state legislative policy, and vaccine cost-benefit analyses are rooted in utilitarianism.

Bentham was a contemporary of British physician Edward Jenner, who took pus from a cowpox lesion and scratched it onto the arm of a young boy in an effort to prevent smallpox. Jenner’s experiment, repeated over and over again in lots of people, created a live human-cow hybrid virus called vaccinia. 79
The new chemical industry took that vaccinia virus, added some chemicals and bottled it, selling it to doctors and governments. The mass smallpox vaccine campaigns that followed expanded the authority of a new branch of medicine focusing on population-based disease control, called public health. 80
19th century physicians were enlisted by government to give infants and children smallpox vaccine and were persuaded to look the other way when some of them died or were left permanently disabled after developing raging vaccinia virus infections and inflammation of the brain. Fully embracing the utilitarian rationale, public health officials viewed individual smallpox vaccine casualties as necessary losses to achieve the greatest good for the greatest number of people.
Utilitarianism Codified Into US Law: Jacobson v. Massachusetts (1905)
At the turn of the 20th century, utilitarianism was fashionable in intellectual and political circles. It was the philosophical argument used by attorneys in 1905 to persuade the U.S. Supreme Court to issue a utilitarian ruling in Jacobson vs. Massachusetts. 81
Lutheran Pastor Henning Jacobsen and his son had suffered severe reactions to previous smallpox vaccinations and Jacobsen argued that genetic predisposition placed him at high risk for dying or being injured if he was forced to get revaccinated. The court dismissed Jacobsen’s concern for his own health and life.
In a split decision with one dissenting vote, the Court that included Oliver Wendell Holmes, issued an opinion that would affirm the legal right for U.S. state legislatures to assign police powers to public health officials to restrict or eliminate individual liberty in order to “secure the general comfort, health and prosperity of the state.” 82

The Court maintained that all citizens can be compelled to receive smallpox vaccinations because the happiness and welfare of the majority outweighs the happiness and welfare of a minority. In other words, individual human sacrifice is ethical and legal if it is done for the common good.
Georgetown law professor and mandatory vaccination proponent Lawrence Gusting has described it as the most important Supreme Court opinion in the history of American public health law. 83
Eugenics: Eradicating the “Unfit” in Buck v. Bell (1927)
In 1927, then Chief Supreme Court Justice Oliver Wendell Holmes used the Jacobson ruling to give the state of Virginia a green light to sterilize Carrie Buck, a 17-year old young single mother who doctors and state social workers had incorrectly judged to be mentally retarded, just like her daughter and mother, they said. 84
Self-identifying as a Darwinian atheist and utilitarian, Chief Justice Holmes’s admiration for exercise of power is reflected in his legal opinions. 85 Holmes did not believe in the concept of natural rights and said, “Between two groups of people who want to make inconsistent kinds of worlds, I see no remedy but force.” 86 He believed scientific knowledge should be used to improve the human race and said, “I can imagine a future in which science shall take control of life, and condemn at once with instant execution what now is left up to nature to destroy.” 87

And, so, when it came to Carrie Buck, Holmes, the eugenicist, coldly proclaimed–
“The principle that sustains compulsory vaccination is broad enough to cover cutting the Fallopian tubes.” 88
In this merciless 1927 Supreme Court decision, just as in the 1905 Jacobson v Massachusetts decision, Holmes achieved his goal of stripping cultural values and ethical principles from U.S. law. His logic was that if utilitarianism could be used to ensure the common good and protect society from infections through compulsory vaccination laws, then forced sterilization laws could be used to immunize society against becoming infected with bad genes.
Social Darwinism and Eugenics in America Inspired Hitler
Darwin’s theory of natural selection led to Social Darwinism 89 and eugenics that was viewed as a new science by U.S. intellectuals during the 1920s and 1930s. 90 American biologist Charles Davenport had founded the Eugenics Record Office at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory on Long Island in 1910 91 to improve the human race and soon courses on eugenics were offered at Harvard, Columbia, Cornell, Brown and other universities. The National Education Association had a Committee on Racial Well-Being to help teachers integrate eugenics content into public school textbooks. 92
By 1932, California and 28 other states had passed compulsory sterilization laws and the practice of eugenics was endorsed by leading U.S. scientists, medical doctors, lawyers, professors, businessmen, politicians, philanthropists, and social reformers like Margaret Sanger. The next year, in 1933, Hitler adopted eugenics as a central piece of his plan to protect the common good by eliminating individuals he considered to be a threat to the health, security and economic well being of the State. By the time eugenics became politically incorrect in the 1940’s, physicians implementing government health policy had performed more than 60,000 involuntary sterilizations on mentally disabled or chronically ill Americans. 93

Hitler was influenced by Marx and Nietzsche and inspired by U.S. eugenics laws. He blended utilitarianism with social Darwinism and nationalism to create a view of the State as one biological entity or body that must be kept healthy and free from disease and threats from unfit individuals.
Enlisting the assistance of physicians and public health officials, the first minority considered unfit and expendable were severely handicapped children, the chronically sick and mentally ill, the “useless eaters” they were called. And when the reasons for why a person was identified as a threat to the health, economic stability, or security of the State grew longer to include minorities who were too old or too Jewish or too Catholic or too opinionated or simply unwilling to believe what those in control of the State said was true….as the list of those the State branded as persons of interest to be demonized, feared, tracked, isolated and eliminated grew, so did the collective denial of those who had yet to be put on that list.
Doctors’ Crimes Against Humanity: Judgment at Nuremberg
When doctors were charged with crimes against humanity at the Doctor’s Trial at Nuremberg for carrying out horrific scientific experiments on captive children and adults in the concentration camps, including vaccine experiments, they pointed to U.S. eugenics laws and invoked a utilitarian defense, claiming it was moral to sacrifice the health and lives of individuals to advance scientific knowledge that could save the lives of many more. 94 95
Out of the Doctors Trial at Nuremberg came the Nuremberg Code, of which Yale law professor and physician Jay Katz said, “if not explicitly then at least implicitly, commanded that the principle of the advancement of science bow to a higher principle: protection of individual inviolability. The rights of individuals to thoroughgoing self-determination and autonomy must come first. “ 96
The First Principle of the Nuremberg Code is, “The voluntary consent of the human subject is absolutely essential.” 97

The Doctor’s Trial at Nuremberg put a human face on individual victims of immoral government health policies. The Nuremberg Code stands as an uncompromising affirmation of the value of every human life and the natural right to self-determination, a timeless guide to ethical behavior by scientists and physicians.
While post World War II Europe had to process what they had learned from The Doctor’s Trial at Nuremberg and the holocaust, things were very different in America. In our country, prominent members of our society who had promoted and participated in the practice of eugenics were never required to look in the mirror and reflect upon what they had done, or face public disgrace. 98 They just went underground.
Science & Math Rule: History of Philosophy Forgotten
Our perception of what is true and good is very much influenced by the prism through which we are taught to view the world.
In today’s public schools, education is focused on science and math, but the study of philosophy and its’ impact on human history is not valued or taught that often. There is no discussion about the kind of utilitarian thinking that made eugenics acceptable in America.

Few Gen Xers and Millennials, who will steer our nation into the second half of the 21nd century, understand the ramifications of allowing utilitarianism to guide public health policy and law, even as the specter of genetic engineering to change what it means to be human is already underway. 99 100 101 Do they understand the influence of utilitarian philosophers like Dr. Peter Singer, professor of bioethics at Princeton, who says it is ethical to euthanize disabled babies in the first 30 days of life, and it is ethical to euthanize elderly and disabled persons who are not aware they serve no useful purpose in society, because, he says, the life of a severely intellectually disabled person has no greater value than that of a dog or pig? 102
Dr. Paul Offit and other contemporary utilitarians who develop vaccines, make vaccine policy and promote “no exceptions” mandatory vaccination laws 103 are forcing us to kneel before them at an altar reminiscent of the one that a 19th century August Comte, built for his Religion of Humanity. We are not allowed to talk about what is true or good in the public square unless we have medical or academic credentials and then - only if we strictly adhere to promoting their consensus science, a code word for censorship that delegitimizes freedom of thought and dissent.
Debate About Forced Vaccination Transcends Vaccination
Today, everybody knows somebody who was healthy, got vaccinated and was never healthy again. But the vaccine science is settled, say the utilitarians refusing to compare the health of vaccinated children to unvaccinated children. Vaccines do not injure and kill, they say, or – if they do – it is so rare, that requiring some children to sacrifice their lives without their parent’s informed consent is ethical in order to enforce mandatory vaccination laws that serve the greater good.
It is for this reason that the debate about vaccination transcends vaccination. It is the tip of the spear in a much larger war that is being waged on cultural values and beliefs in America, which is why I call it The Vaccine Culture War.
Because if the State can tag, track down and force citizens against their will to be injected with biologicals of known and unknown toxicity today, then there will be no limit on which individual freedoms the State can take away in the name of the greater good tomorrow.
Today the battlefield of the 200 year war on microbes is littered with human casualties far too numerous to count while, in a natural fight to survive, the microbes have evolved to evade the vaccines. 104 And the scientists and physicians in leadership positions determined to win that war continue to fire away, stepping around the bodies of vaccine-damaged children lying on the ground.
Do I think that public health officials flying the science flag with a utilitarian star on it wake up everyday and say to themselves, I want to hurt a child today? Of course not. Most doctors and scientists want to help, not harm people.

Do I think they have lost their way, blinded by a utilitarian pseudo-ethic that makes it easy to ignore the bodies lying on the ground so they can allow themselves to believe that human sacrifice is ethical when it serves the greater good? Yes, I do. They have forgotten to ask themselves this question:
When one individual is considered expendable for the good of society, how many more can be considered expendable? Is it 500, 5,000, 50 million - or more? How many is too many to sacrifice for the happiness of the rest, and who gets to decide which ones among us are expendable?
Holocaust survivor Elie Weisel said, “When you take an idea or concept and turn it into an abstraction, that opens the way to take human beings and turn them, also, into abstractions. When people are turned into abstractions, what is left?” 105
He is right. Abstractions are much easier to write off as coincidences. Abstractions are easier to add up in a column when there is no name or a face put to them. Abstractions do not live or breathe, bleed or convulse, scream or die. Abstractions can be dismissed and buried in files where nobody ever has to look.
Rejecting Utilitarianism & Embracing An Authentic Ethic
After surviving four concentration camps, physician Viktor Frankl called on mankind to reject the materialist view that a person only has value if he useful to society, which makes him a slave to the State. Frankl said:
“The gas chambers of Auschwitz were the ultimate consequence of the theory that man is nothing but the product of heredity and environment—or, as the Nazis liked to say, of ‘Blood and Soil.’” I am absolutely convinced that the gas chambers of Auschwitz, Treblinka, and Majdanek were ultimately prepared not in some Ministry or other in Berlin, but rather at the desks and in the lecture halls of nihilistic scientists and philosophers.” 106

Transcending the horror of what he had witnessed, Dr. Frankl was able to see that, “Between stimulus and response, there is a space. In that space is our power to choose our response. In our response lies our growth and our freedom.“ ..... “It is this spiritual freedom – which cannot be taken away – that makes life meaningful and purposeful.
In the 21st century, all of us are called upon to choose whether or not we will embrace what Albert Schweitzer called “a reverence for life.” 107 It requires us to turn away from materialist philosophers like Hobbes, Bentham, Comte, Marx, Nietzsche and Singer, who say that individual life does not matter, that life has no meaning, and that morality can be reduced to a mathematical equation. Enlightened physicians and scientists with compassion and courage are called upon to take back leadership of their professions from those who have lost their way. Even as those, who have been victims of utilitarian health policies, must continue to witness in the public square.
Only then can we reject utilitarianism as a guide to the practice of medicine so consensus science orthodoxy will give way to real science that yields the truth about vaccination and health. Only then can we transcend the horror of what has happened to far too many children in the name of the greater good and adopt an authentic ethic, one that values individual autonomy and freedom of thought, speech and conscience - civil liberties that have been an antidote to tyranny in its many forms throughout human history.
Our mission continues. No forced vaccination. Not in America.
References:
1 Fisher BL. The Moral Right to Conscientious, Philosophical and Personal Belief Exemption to Vaccination. National Vaccine Advisory Committee (NVAC), U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Oral Presentation May 2, 1997.
2 Nir E. Informed Consent. Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy Sept. 21, 2011.
3 Cohen J, Ezer T. Human Rights in Patient Care: A Theoretical and Practical Framework. Health and Human Rights Journal 2013; 15(2).
4 HG.org. Understanding Informed Consent.
5 U.S. Library of Medicine. Informed Consent – Adults. Medline Plus Oct. 29, 2015.
6 Morrison P. Historian Elena Conis takes a look at decades of vaccination skepticism. LA Times Jan. 27, 2015.
7 Fisher BL. Class and Race Profiling in the Vaccine Culture War. NVIC Newsletter July 17, 2017.
8 Biography Online. Albert Einstein quoted by Virgil Henshaw in Albert Einstein: Philosopher Scientist (1949) edited by Paul A. Schilpp.
9 CDC. Possible Side Effects of Vaccines. May 8, 2017.
10 HRSA. National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program: Vaccine Injury Compensation Data. October 2017.
11 Institute of Medicine. Genes, Behavior and the Social Environment: Moving Beyond the Nature/Nurture Debate. National Academies Press (US) 2006.
12 Paul B, Barnes S et al. Influence of diet and the gut microbiome on epigenetic modulation in cancer and other diseases. Clin Epigenetics 2015; 7:112.
13 CDC. Vaccine Excipient & Media Summary: Excipients Included in U.S. Vaccines, by Vaccine. Jan. 6, 2017.
14 Eberly College of Science. Elementary Microbiology: Categories of Specific Immunity. University of Pennsylvania 2017.
15 Fisher BL. Pertussis Microbe Outsmarts Vaccines As Experts Argue About Why. NVIC Newsletter Mar. 27, 2017.
16 Institute of Medicine Vaccine Safety Committee. Adverse Effects of Pertussis and Rubella Vaccines. Afterword on Research Needs (p. 206). Washington, DC. The National Academies Press 1991.
17 Institute of Medicine Vaccine Safety Committee. Adverse Events Associated with Childhood Vaccines: Evidence Bearing on Causality. Need for Research and Surveillance. Washington, D.C. The National Academies Press 1994.
18 Institute of Medicine Vaccine Safety Forum. Summaries of Two Workshops. Research Opportunities (p. 44).Washington, D.C. The National Academies Press 1997.
19 Institute of Medicine Committee to Review Adverse Effects of Vaccines. Adverse Effects of Vaccines: Evidence and Causality. Evaluation of Biologic Mechanisms of Adverse Effects: Increased Susceptibility (p. 82). Washington, D.C. The National Academies Press 2012.
20 Institute of Medicine Committee on the Assessment of Studies of Health Outcomes Related to the Recommended Childhood Immunization Schedule. The Childhood Immunization Schedule and Safety Stakeholder Concerns, Scientific Evidence and Future Studies: Summary (p. 5-6) and Summary of Scientific Findings (p. 129-130). Washington, D.C. The National Academies Press 2013.
21 Institute of Medicine Committee Priorities for the National Vaccine Plan. The Safety of Vaccines and Vaccination Practices (p. 53). The National Academies Press 2010.
22 Ellenberg S. Clinical Trials of Childhood Vaccines. Institute of Medicine Committee on the Assessment of Studies of Health Outcomes Related to the Recommended Childhood Immunization Schedule Public Meeting Feb. 9, 2012.
23 Institute of Medicine Committee on the Assessment of Studies of Health Outcomes Related to the Recommended Childhood Immunization Schedule. The Childhood Immunization Schedule and Safety Stakeholder Concerns, Scientific Evidence and Future Studies: Summary (p. 5-6) and Summary of Scientific Findings (p. 129-130). Washington, D.C. The National Academies Press 2013.
24 CDC. Vaccine Recommendations and Guidelines of the ACIP. Contraindications and Precautions: Conditions incorrectly perceived as contraindications to vaccines (i.e., vaccines may be given under these conditions). Apr. 20, 2017.
25 Fisher BL. Blackmail and the Medical Vaccine Exemption. NVIC Newsletter May 18, 2015.
26 NVIC. National Vaccine Information Center Cites “Betrayal’ of Consumers by US Supreme Court Giving Total Liability Shield to Big Pharma. Business Wire Feb. 23, 2011.
27 LaVigne P. Global Vaccine Market Surges to More than $70 Billion by 2024. The Vaccine Reaction Nov. 10, 2016. change
28 Fisher BL. Vaccine Injury Compensation: Government’s Broken Social Contract with Parents. NVIC Newsletter Nov. 2, 2015
29 Halabi SF, Omer SB. A Global Vaccine Injury Compensation Program. JAMA 2017; 317(5): 471-472.
30 Mastrioianni AC, Henry LM. Legal Complexities of Global Vaccine Compensation Systems. JAMA 2017; 317(18): 1911-1912.
31 Ramezanpour B, Haan I et al. Vector-based genetically modified vaccines: Exploiting Jenner’s legacy. Vaccine 2016; 34: 6436-6448.
32 Moyle PM. Biotechnology approaches to produce potent, self-adjuvanting antigen-adjuvant fusion protein subunit vaccines. Biotechnol Adv 2017; 35(3): 375-389.
33 Chan VS. Use of genetically modified viruses and genetically engineered virus-vector vaccines: environmental effects. J Toxicol Environ Health A 2006; 69(21): 1971-1977.
34 Trafton A. One Injection Could Carry Many Doses. MIT News Sept. 14, 2017.
Fisher BL. Defending the Religious Exemption to Vaccination. NVIC Newsletter June 28, 2016.
36 Richardson D. The Fallout from California SB277: What Happens Next? NVIC Newsletter Aug. 5, 2015.
37 Physicians for Informed Consent Inaugural Meeting Mar. 12, 2017 in Costa Mesa, CA.
38 Utilitarian Philosopy.com. Utilitarian Philosophy.
39 Kay CD. Notes on Utilitarianism. Wofford College Department of Philosophy 1997.
40 Anderson K. Utilitarianism: The Greatest Good for the Greatest Number. Probe Ministries International 2004.
41 Conis E. Vaccination Resistance in Historical Perspective. The American Historian 2015 (August).
42 Cody CL, Baraff LJ, Cherry JD et al. Nature and Rates of Adverse Reactions Associated with DTP and DT Immunizations in Infants and Children . Pediatrics 1981; 68(5).
43 Miller DL, Ross EM, Alderslade R et al.Pertussis immunization and serious acute neurological illness in children. Brit Med J 1981; 282: 1595-1599.
44 Institute of Medicine Vaccine Safety Committee. Adverse Effects of Pertussis and Rubella Vaccines. Chapter 4: Encephalopathy (pp. 86-88). Washington, DC. The National Academies Press 1991.
45 Institute of Medicine Committee to Study New Research on Vaccines. DPT Vaccine and Chronic Nervous System Dysfunction: A New Analysis. Executive Summary (pp.1-2) Washington, D.C. The National Academies Press 1994.
46 Harvard University Library. Contagion: Historical Views of Diseases and
47 Latimer FR, Webster JE, Gurdjian ES. Neurological Complications of Rabies Vaccine: Report of Two Cases. AMA Arch NeurPsych 1951; 65(1): 16-28
48 Roos KL, Eckerman NL. The Smallpox Vaccine and Postvaccinal Encephalitis. Semin Neurol 2002; 22(1): 095-098.
49 Huynh W, Cordato DJ et al. Post-vaccination encephalomyelitis: Literature review and illustrative case. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience 2008; 15: 1315-1322.
50 Halpern, S.R., and Halpern, D. Reactions from DPT immunization and its relationship to allergic children. Journal of Pediatrics 1955; 47:60-67.
51 Hopper JM. Illness after whooping cough vaccination. Medical Officer 1961 (October 20); 241-244.
52 Illingworth R. Contraindications to immunization. Brit Med J (July 24): 229.
53 Steinman L, Sriram S et al. Murine model for pertussis vaccine encephalopathy: Linkage to H-2. Nature 1982; 299: 738-740.
54 Institute of Medicine Vaccine Safety Forum. Howe CJ, Johnston RB, Fenichel GM, Editors. Summaries of Two Workshops. Research to Identify Risks for Adverse Events Following Vaccination- Biological Mechanisms and Possible Means of Prevention: Genetic Factors Affecting Development of Autoimmunity. Washington, D.C. The National Academy Press 1997.
55 Institute of Medicine Committee to Review Adverse Effects of Vaccines. Evaluation of Biologic Mechanisms of Adverse Effects: Increased Susceptibility. (p. 82). Washington, D.C. The National Academies Press 2013.
56 Soriano A, Nesher G, Shoenfeld Y. Predicting post-vaccination autoimmunity: Who might be at risk? Pharmacological Research 2014.
57 Trebbe AL. Local TV Honors Its Own: Channels 4 and 7 Sweep the Emmys. Washington Post June 27,1983.
58 Byers, R.K., and Moll, F.C. Encephalopathies following prophylactic pertussis vaccination. Pediatrics 1948; 1(4):437-56.
59 Halpern, S.R., and Halpern, D. Reactions from DPT immunization and its relationship to allergic children. Journal of Pediatrics 1955; 47:60-67.
60 Cody CL, Baraff LJ, Cherry JD et al. Nature and Rates of Adverse Reactions Associated with DTP and DT Immunizations in Infants and Children . Pediatrics 1981; 68(5).
Berg, J.M. 1958. Neurological complications of pertussis immunization. British Medical Journal 1958; 2 (5087): 24-27.
62 Strom, J. Further experience of reactions, especially of a cerebral nature, in conjunction with triple vaccination: study based on vaccinations in Sweden, 1959-1965. British Medical Journal 1967; 4:320-23.
63 Stewart, G.T., et al. 1981. Pertussis vaccine and acute neurological disease in children. British Medical Journal 1981(June 13): 1968-69.
64 Koplan JP, Schoenbaum SC et al. Pertussis Vaccine - An Analysis of Benefits, Risks and Costs. New Eng J Med 1979; 301: 906-911.
65 Fisher BL. Harris Coulter Was a Brave Visionary. NVIC Newsletter Mar. 29, 2010.
66 Institute of Medicine Vaccine Safety Committee. Adverse Effects of Pertussis and Rubella Vaccines. Pertussis and Rubella Vaccines A Brief Chronology: 1985; Appendix B, pp. 325. Washington, DC. The National Academies Press 1991.
67 HRSA. National Vaccine Injury Compensation Program: Vaccine Injury Compensation Data. October 2017.
68 Fisher, BL. Vaccine Revolution for Truth. See References. NVIC Newsletter Apr. 19, 2017.
69 Centers for Disease Control (CDC). Recommended schedule for active immunization of normal infants and children. DHHS 1983.
70 CDC. Recommended Immunization Schedules for Persons Aged 0 Through 18 Years, United States, 2017
71 NVIC. Barbara Loe Fisher – Bio.
72 Philosophical Society.com. History of Philosophy (abbreviated).
73 Burnett T. What is Scientism? AAAS Mar. 30, 2016.
74 National Archives. America’s Founding Documents: Declaration of Independence, Constitution, Bill of Rights.
75 Constitution of Virginia. Article 1 Bill of Rights; Section 16: Free exercise of religion; no establishment of religion.
76 United Nations. Universal Declaration of Human Rights. 1948.
77 Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Jeremy Bentham (1748-1832).
78 Crimmins JE. Bentham on Religion: Atheism and the Secular Society. Journal of the History of Ideas 1986; 47(1): 95-110.
79 Fisher BL. Smallpox (Variola) and Live Attenuated Vaccinia Virus. The Emerging Risks of Live Virus & Virus Vectored Vaccines: Vaccine Strain Virus Infection, Shedding & Transmission. pp. 16-21. NVIC.org November 2014.
80 Institute of Medicine (US) Committee for the Study of the Future of Public Health. A History of the Public Health System. The Future of Public Health. National Academies Press 1988.
81 Fisher BL. Forced Vaccination: The Tragic Legacy of Jacobson v. Massachusetts. NVIC Newsletter Nov. 2, 2016.
82 Jacobson v. Massachusetts. 197 U.S. 11(1905). Cornell University Law School.
83 Gostin LO. Jacobson v. Massachusetts at 100 Years: Police Power and Civil Liberties in Tension. Am J Public Health 2005; 95(4): 576-581.
University of Virginia. Eugenics: Buck v Bell, The Test Case for Virginia’s Eugenical Sterilization Act. Claude Moore Health Science Library 2004
85 Uhlmann MM. The Darwinian Mind and Faith of Justice Holmes. Claremont Review of Books May 21, 2001; 1(3).
86 Holmes-Pollack Letters (1941). 2H – P.L. 36, 41.
87 Holmes, OW, Jr. A Soldier’s Faith. Harvard Graduation Address May 30, 1895.
88 Supreme Court Upholds Sterilization of the Mentally Retarded – Buck v. Bell, 274 U.S. 200, 475 Ct. 584, 71L, Ed. 1000 (1927). LSU Law Center.
89 Bowler P. Social Darwinism. Oxford Bibliographies May 26, 2016.
90 Bouce T, Rivard L. America’s Hidden History: The Eugenics Movement. Nature Sept. 18. 2014.
91 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Library Archives. Eugenics Records Office.
92 Selden S. Eugenics Popularization. Eugenics Archive Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory.
93 Black E. Eugenics and the Nazis – The California Connection. SF Gate Nov. 9, 2003.
94 Annas GJ, Grodin MA. The Nazi Doctors and the Nuremberg Code. Oxford University Press 1992.
95 Schultz JJ. The Doctor’s Dilemma: The Utilitarian Medical Ethics of Nazi Physician Karl Brandt. University of Toronto Journal 2013; 90(4): 176.
96 Katz J. Now. In: Nazi Doctors and the Nuremberg Code – Human Rights in Human Experimentation. Oxford University Press 1992: Page 236.
97 Schuster E. Fifty Years Later: The Significance of the Nuremberg Code. N Engl J Med 1997; 337: 1438-1440.
98 DenHoed A. The Forgotten Lessons of the American Eugenics Movement. The New Yorker Apr. 27, 2016.
99 Resnik DB, Vorhaus DB. Genetic modification and genetic determinism. Philosophy, Ethics, and Humanities in Medicine 2006; 1(9).
100 Regalado A. Engineering the Perfect Baby. MIT Technology Review Mar. 5, 2015.
101 Kozubek J. How Gene Editing Could Ruin Human Evolution. Time Magazine Jan. 9, 2017.
102 Klusendorf S. Peter Singer’s Bold Defense of Infanticide. Christian Research Institute Apr. 16, 2009.
103 Fisher BL. The Vaccine Culture War in America: Are You Ready? NVIC Newsletter Mar. 8, 2015.
104 Fisher BL. Pertussis Microbe Outsmarts the Vaccines As Experts Argue About Why. NVIC Newsletter Mar. 27, 2016.
105 Annas GJ, Grodin MA. The Nazi Doctors and the Nuremberg Code – Human Rights in Human Experimentation. Elie Wiesel: Forward. Oxford University Press 1992.
106 Frankl, V. (1959). Man’s search for meaning. New York: Random House.
107 The Albert Schweitzer Fellowship. Reverence for Life.










Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked with an *