Read and report vaccine reactions, harassment and failures.
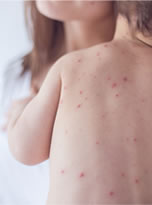
Chickenpox (Varicella) is a highly contagious infection that is generally mild for most children. Chickenpox is transmitted through direct contact with or by inhaling particles from the chickenpox blisters. It may also possibly be spread through the respiratory secretions of a person infected with the virus. Less commonly, a person who lacks immunity to chickenpox can also develop the illness by coming into contact with a shingles rash. Symptoms of chickenpox generally begin between 10- and 21-days following exposure to the virus and the illness typically lasts between 5 and 10 days.
Initial chickenpox symptoms can include headache, fever, loss of appetite, and fatigue. When the chickenpox rash occurs, it usually begins with raised red or pink itchy bumps (papules). These bumps generally last a few days before progressing to become fluid-filled blisters (vesicles). After about a day or so, the blisters break open, leak and eventually crust and scab over. The rash usually starts on the head, then spreads to the trunk, and eventually to the arms and legs. The rash can also be present in the eyes, throat, and genitals. As the rash appears over several days, chickenpox lesions can be simultaneously present on the body as papules, vesicles, and scabs.
Chickenpox is considered contagious for 1 to 2 days prior to the onset of the rash and remains so until all lesions have become scabs. Individuals previously vaccinated with the chickenpox vaccine and who develop chickenpox are considered to be contagious until 24 hours following the final appearance of lesions. Chickenpox lesions in a person previously vaccinated with the chickenpox vaccine may not always crust over.
Previously vaccinated individuals who develop chickenpox are still contagious and can spread the infection to others.
IMPORTANT NOTE: NVIC encourages you to become fully informed about Chickenpox and the Chickenpox vaccine by reading all sections in the Table of Contents , which contain many links and resources such as the manufacturer product information inserts, and to speak with one or more trusted health care professionals before making a vaccination decision for yourself or your child. This information is for educational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice.



